Unlike earlier smart cars that featured an automatically actuated single clutch manual transmission, the later “Twinamic” version introduced in the 2014 to 2019 (A453) Smart ForTwo and ForFour models employs a Getrag 6DCT250 6-speed dry dual clutch automatic transmission. This advanced transmission is also used in the 2014+ Renault Twingo—sharing the same engine as the Smart—as well as in the Ford Fiesta, Focus, and EcoSport, where it is known as the Powershift transmission, mounted to a different engine platform.
As far as DCT’s (dual clutch transmissions) go it is a fairly simple design with two motor driven clutch actuator forks and an all in one shifter module with two internals motors which drive the selector drums in the gearbox.
There are also three speed sensors which I assume are one for each output shaft and one for the input shaft.
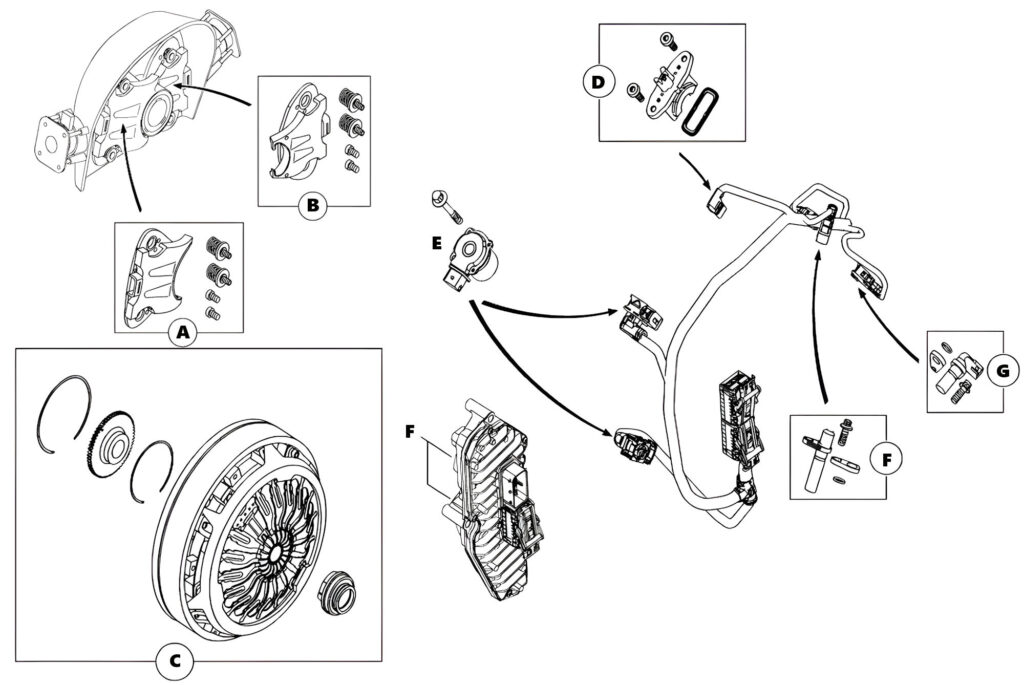
- A. Clutch actuator (outer) (A4539065201)
- B. Clutch actuator (inner) (A4539065101)
- C. Dual clutch assembly. (A4532500600)
- D. RPM Sensor (A4159056100)
- E. Clutch actuator motors (M14=Upper, M15=Lower) (A4539063001)
- F. Combined TCU and shifter motors (A2C73768910)
- G. RPM Sensor (A4539053101)
- F. RPM Sensor (A4539053301)
For more information about replacing the clutch/actuator forks please check out this post:
Smart 453 DCT Clutch Replacement & Adaption
Clutch Actuator Motor failure symptoms
The M14 & M15 motors that drive the clutch actuator forks are the simplest to fix failure point on this transmission and usually manifest as an obviously corroded motor, a rattling noise and loss of either even (Reverse, 2nd, 4th & 6th) or odd (1st, 2nd, 3rd & 5th) gears.
And an error along the lines of “Clutch travel sensor signal 2 – Signal comparison failed” stored DTC.
The motor for Clutch 2 (M15) is mounted near the bottom of the transmission and is literally a 5 minute job to change (4 E8 Torx bolts). Unfortunately the upper motor (M14) for Clutch 1 is buried under the intake manifold so removing it is fairly involved (see the video further down this post).
WARNING: If you remove the clutch pack from the transmission is requires resetting to “transport mode” before it can be refitted.
Clutch Actuator Fork failure symptoms
The clutch actuator forks are in essence a worm gear attached to sled with roller bearings that is forced between the back of the bell housing and the corresponding clutch release bearing which forces the bearing into the clutch fingers.
These actuators can be come jammed up causing shift failures and adaption issues with fault codes such as:
- P195278: The specified position of component ‘clutch 1’ cannot be reached. The adaption or adjustment is incorrect.
- P195592: The maximum position of the component ‘M14 (Clutch actuator 1)’ is implausible. The function or instruction is faulty.
It is possible to test the actuators using a special splined tool that replicates the output shaft of the actuator motors: the load of the clutch on the forks should always reset them to their “neutral position” (fully wound clockwise) and when you try and turn them anti-clockwise you should feel them trying to unwind back to their “neutral position” – if the fork doesn’t unwind, it is hard to turn or doesn’t feel smooth to turn you can assume the actuator has failed.
Clutch Actuator Motor Tear-down
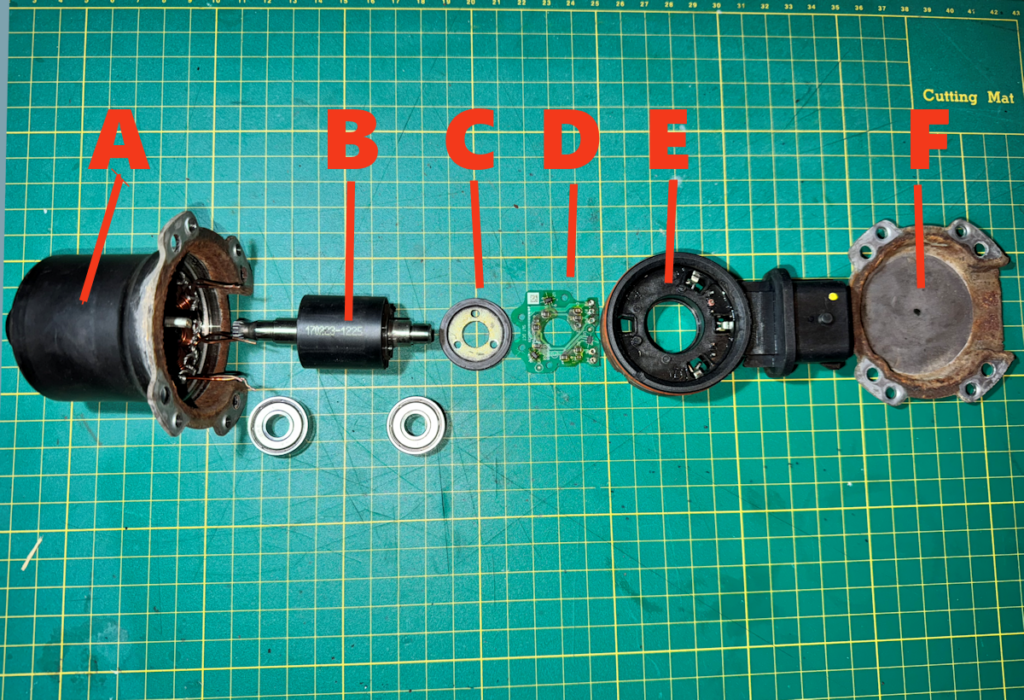

- A. Housing & stator windings
- B. Motor core / poles
- C. Reference magnet
- D. PCB / Hall effect sensors
- E. Base
- F. Lower plate
Removing The Lower (M15) Clutch 2 Actuator Motor
Removing the lower actuator motor for clutch 2 is very simple as it is accessible from underneath the car.
Simply disconnect the loom, remove the 4 torx bolts and withdraw the motor.
Removing The Upper (M14) Clutch 1 Actuator Motor
Unfortunately the upper actuator motor for clutch 1 is quite an ordeal due to it being covered up by the intake manifold with very little clearance.
The following video explains more:

Pingback: Smart 453 DCT Clutch Replacement & Adaption – My Blog
Hello, thank you for this helpful explanation. Does actuator 2 need to be calibrated after replacement? Regards
It’s good practice to do the travel calibration after replacing and actuator.